Covert timing channels: analyzing WEB traffic

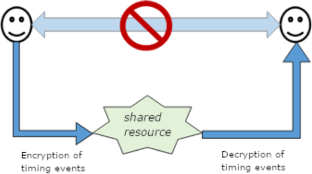
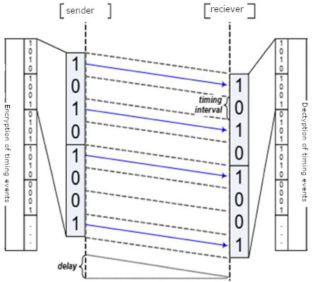
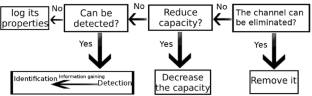
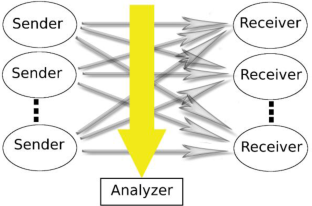
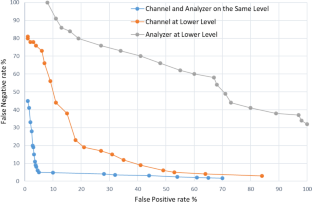
In case there is a communication contrary to the system security policies, a covert channel has been created. The attacker can easily disclosure information from the victim’s system with just one public access permission. Covert timing channels, unlike covert storage channels, do not have memory storage and they draw less attention. Different methods have been proposed for their identification, which generally benefit from the shape of traffic and the channel’s regularity. The application nature of HTTP protocol allows the creation of a covert timing channel based on different features of this protocol (or different levels) that has not been addressed in previous researches. This research tries to study the effect of using different features (or levels) of HTTP protocol on identifying the covert channel. The amount of channel’s entropy could be manipulated by changing the channel’s level or adding intentional noise on the channel to protect from the analyzer’s detection. The difference in the placement of the covert channel and the detector causes the amount of channel entropy to be far from the detection threshold. Therefore, we concluded that the analyzer must investigate traffic at all possible levels. Adding noise on the covert channel decrease its capacity, but as entropy increases, it would be harder to detect it.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save
Springer+ Basic
€32.70 /Month
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Buy Now
Price includes VAT (France)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve

Similar content being viewed by others

Evaluation of Statistical Tests for Detecting Storage-Based Covert Channels
Chapter © 2020

A Muti-detection Method of Covert Timing Channel Based on Perceptual Hashing
Chapter © 2021
Investigative support for information confidentiality
Article 09 July 2015
Notes
Simple mail transfer protocol.
File transfer protocol.
References
- Sommer, F., Jürgen, D., Reiner, K.: Survey and classification of automotive security attacks. Information 10(4), 148 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/info10040148ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Mikhail, F., Flor, A., Steinmetzer, D., Paul Gardner, S., Hollick, M.: Survey and systematization of secure device pairing. Commun. Surv. Tutor. IEEE 20(1), 517–550 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2017.2748278ArticleGoogle Scholar
- US Department of Defense.: Trusted Computer System Evaluation Criteria. ISBN 978-0-333-53947-7, Palgrave Macmillan, London (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-349-12020-8_1.
- Gligor,V.D.: A guide to understanding covert channel analysis of trusted systems. National Computer Security Center (US). Meade, Maryland, NCSC-TG-030 (1994)
- Carrara, B., Adams, C.: A survey and taxonomy aimed at the detection and measurement of covert channels. In: Proceedings of the 4th ACM Workshop on Information Hiding and Multimedia Security, pp. 115–126 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1145/2909827.2930800
- Okhravi, H., Bak, S., King, S.T.: Design, implementation and evaluation of covert channel attacks. In: IEEE International Conference on Technologies for Homeland Security (HST), pp. 481–487 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/THS.2010.5654967
- Wang, Z., Lee, R.B.: New constructive approach to covert channel modeling and channel capacity estimation. In: International Conference on Information Security, pp. 498–505 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/11556992_37
- Changxiang, S., et al.: Survey of information security. Sci. China Ser. F Inf. Sci. 50(3), 273–298 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-007-0037-2ArticleMATHGoogle Scholar
- Xiaosong, Z., et al.: A covert channel over volte via adjusting silence periods. IEEE Access 6, 9292–9302 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2802783ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Mazurczyk, W. et al.: Information Hiding in Communication Networks: Fundamentals, Mechanisms, Applications, and Countermeasures, Wiley (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119081715
- Cabuk, S., Brodley, C.E., Shields, C.: IP covert timing channels: design and detection. In: Proceedings of the 11th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, pp. 178–187 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1145/1030083.1030108
- Berk, V., Giani, A., Cybenko, G., Hanover, N.: Detection of covert channel encoding in network packet delays. Rapport technique TR536, de lUniversité de Dartmouth, p. 19 (2005)
- Coleman, T.P., Kiyavash, N.: Sparse graph codes and practical decoding algorithms for communicating over packet timings in networks. In: 42nd Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems, CISS 2008, pp. 447–452 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/CISS.2008.4558568
- Yao, S., Yang, W., Liusheng, H.: Concealed in web surfing: behavior-based covert channels in HTTP. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 101, 83–95 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2017.10.019ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Chen, A. et al.: Detecting covert timing channels with time-deterministic replay. In: 11th Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation ( 14) (2014)
- Beyrami, B., Dehghani, M., Saleh Esfahani, M.: Covert timing channel detection based on statistical methods. J. Electron. Cyber Defence 2(5), 13–24 (2014). ((in Persian)) Google Scholar
- Kiyavash, N., Coleman, T.: Covert timing channels codes for communication over interactive traffic. In: ICASSP IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal processing, pp. 1485–1488 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2009.4959876
- Cabuk, S., Brodley, C.E., Shields, C.: IP covert channel detection. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. Secur. (TISSEC) 12(4), 22 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1145/1513601.1513604ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Nasseralfoghara, M., Hamidi, H.: Web covert timing channel detection based on entropy. Electron. Cyber Defense 8(3), 13–23 (2021). (in Persian) Google Scholar
- Nasseralfoghara, M., Hamidi, H.: Entropy-based analyzing anomaly WEB traffic. High Speed Netw. 26(4), 255–266 (2020) ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Brown, E., Yuan, B., Johnson, D., Lutz, P.: Covert channels in the HTTP network protocol: channel characterization and detecting man-in-the-middle attacks. In: International Conference on Cyber Warfare and Security, p. 56 (2010)
- Gianvecchio, S., Wang, H., Wijesekera, D., Jajodia, S.: Model-based covert timing channels: automated modeling and evasion. In: International Workshop on Recent Advances in Intrusion Detection, pp. 211–230 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-87403-4_12
- Coleman, T.P., Kiyavash, N.: Practical codes for queueing channels: an algebraic, state-space, message-passing approach. In: Information Theory Workshop, ITW'08, IEEE, pp. 318–322 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/ITW.2008.4578677
- Liu, Y., Ghosal, D., Armknecht, F., Sadeghi, A.-R., Schulz, S., Katzenbeisser, S.: Hide and seek in time—robust covert timing channels. In: European Symposium on Research in Computer Security, pp. 120–135 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04444-1_8
- Liu, Y., Ghosal, D., Armknecht, F., Sadeghi, A.-R., Schulz, S., Katzenbeisser, S.: Robust and undetectable steganographic timing channels for iid traffic. In: International Workshop on Information Hiding, pp. 193--207 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-16435-4_15
- Saadati, M., Dehghani, M., Saleh Esfahani, M.: Simulation and evaluation of jitter and packet loss noises influence on covert timing channel performance. J. Electron. Cyber Defence 2(3), 35–49 (2014). ((in Persian)) Google Scholar
- Liu, J., et al.: A detection-resistant covert timing channel based on geometric huffman coding. In: International Conference on Wireless Algorithms, Systems, and Applications, Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-94268-1_26
- Archibald, R., Ghosal, D.: A covert timing channel based on fountain codes. In: IEEE 11th International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications (TrustCom), pp. 970–977 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/TrustCom.2012.21
- Ahn, T.S. et al.: Turbo equalization for covert communication in underwater channel. In: Eighth International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks (ICUFN), IEEE (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICUFN.2016.7537071
- Wang, J. et al.: Implementing a covert timing channel based on mimic function. In: International Conference on Information Security Practice and Experience, Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-06320-1_19
- Han, T.S., Kobayashi, K.: Mathematics of information and coding. Am. Math. Soc. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1090/mmono/203,PMid:17014848ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Stillman, R.M.: Detecting IP covert timing channels by correlating packet timing with memory content. In: Southeastcon, IEEE, pp. 204–209 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/SECON.2008.4494286
- Liu,G., Zhai, J., Dai, Y., Wang, Z.: Covert timing channel with distribution matching. In: International Conference on Multimedia Information Networking and Security, MINES'09, vol.1, pp. 565–568 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/MINES.2009.28
- Liu, G., Zhai, J., Dai, Y.: Network covert timing channel with distribution matching. Telecommun. Syst. 49(2), 199–205 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-010-9368-1ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Zander, S., Armitage, G., Branch, P.: Stealthier inter-packet timing covert channels. Networking 2011, 458–470 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-20757-0_36ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Walls, R.J., Kothari, K., Wright, M.: Liquid: a detection-resistant covert timing channel based on IPD shaping. Comput. Netw. 55(6), 1217–1228 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2010.11.007ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Lee, K.S., Wang, H., Weatherspoon, H.: covert channels: can you see the idles? In: 11th Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation ( 14), pp. 173–185 (2014)
Funding
This research received no external funding.











